반응형
- 브로드캐스팅은 데이터 처리에서 중요한 위치에 있다. 익숙해지기 위해 여러 가지 예시를 들며, 결과를 확인해보겠다.
- 예 1
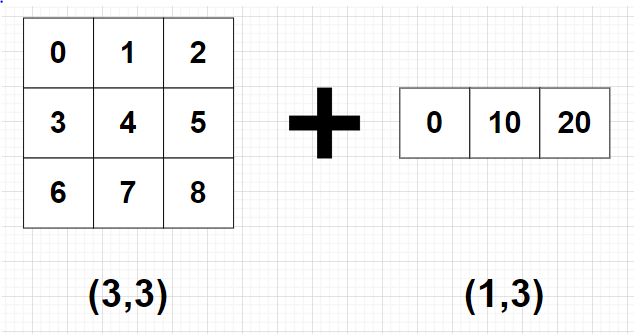
import numpy as np
A = np.arange(9).reshape(3, 3)
B = 10*np.arange(3).reshape((-1, 3))
C = A + B
print(C)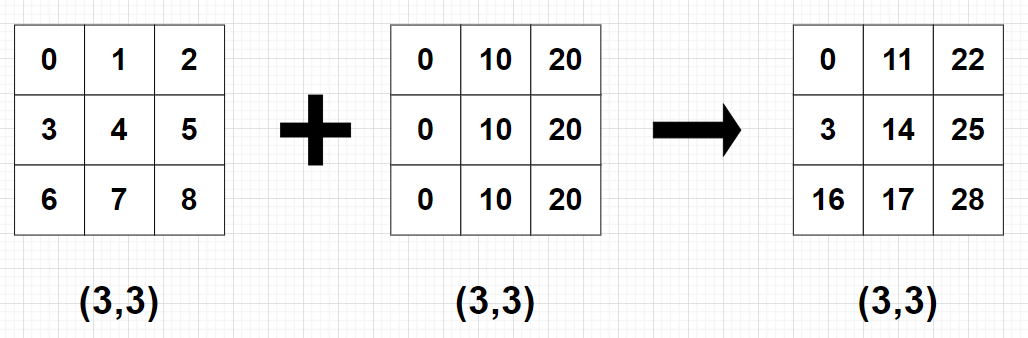
print(C) # [[ 0 11 22]
# [ 3 14 25]
# [ 6 17 28]]- 예 2
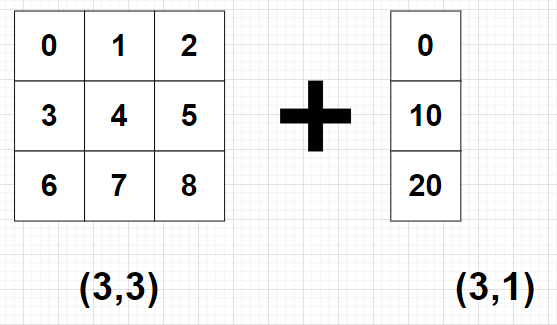
import numpy as np
A = np.arange(9).reshape(3, 3)
B = 10*np.arange(3).reshape((3, -1))
C = A + B
print(C)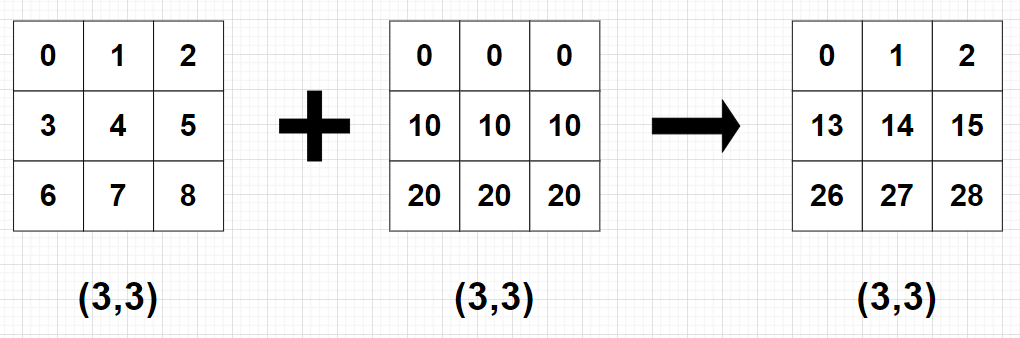
print(C) #[[ 0 1 2]
# [13 14 15]
# [26 27 28]]- 예 3
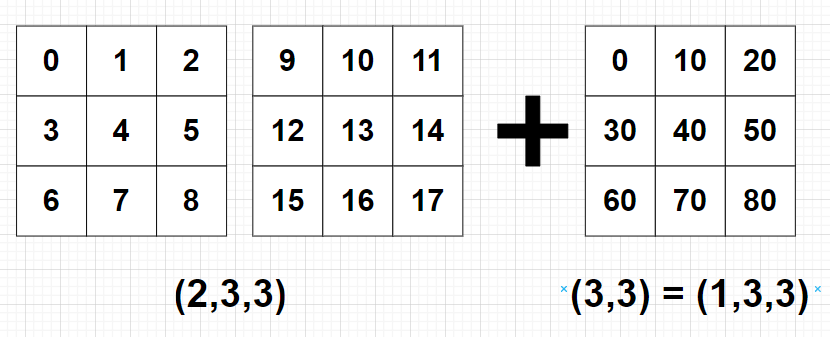
import numpy as np
A = np.arange(18).reshape((2, 3, 3))
B = 10*np.arange(9).reshape((1, 3, 3))
C = A + B
print(C)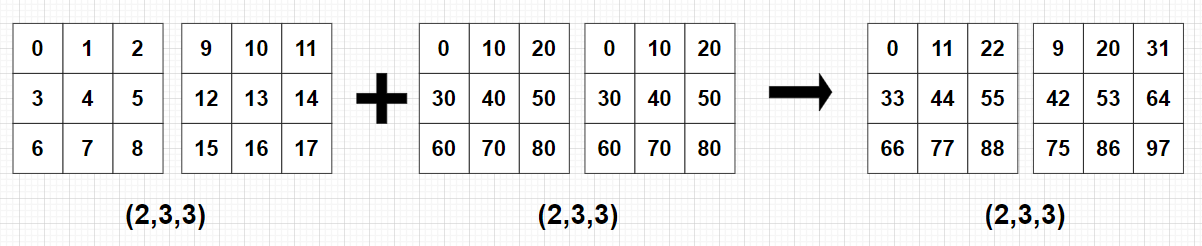
print(C) # [[[ 0 11 22]
# [33 44 55]
# [66 77 88]]
# [[ 9 20 31]
# [42 53 64]
# [75 86 97]]]- 예 4
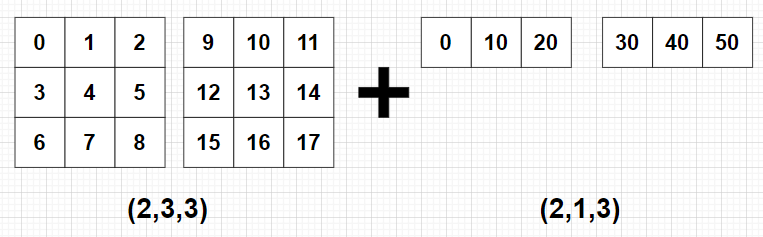
import numpy as np
A = np.arange(2*3*3).reshape((2, 3, 3))
B = 10*np.arange(2*1*3).reshape((2, 1, 3))
C = A + B
print(C)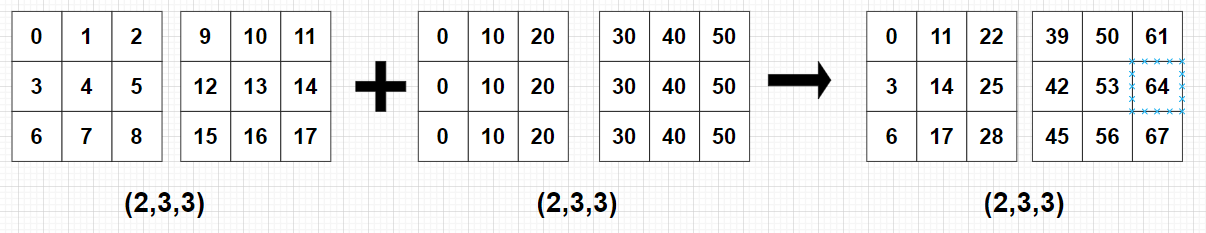
print(C) # [[[ 0 11 22]
# [ 3 14 25]
# [ 6 17 28]]
# [[39 50 61]
# [42 53 64]
# [45 56 67]]]- 예 5
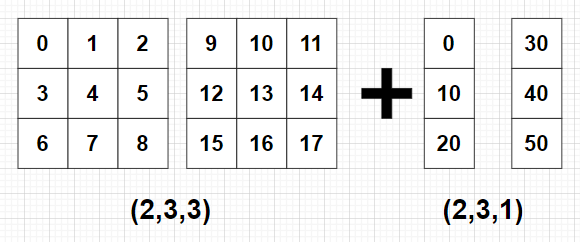
import numpy as np
A = np.arange(18).reshape((2, 3, 3))
B = 10*np.arange(6).reshape((2, 3, 1))
C = A + B
print(C)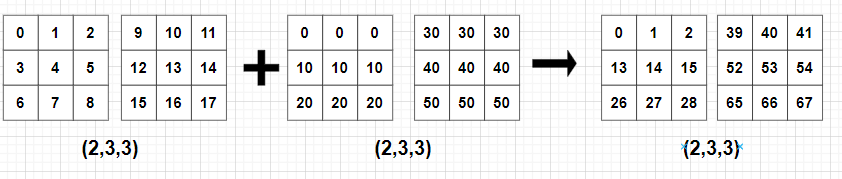
print(C) # [[[ 0 1 2]
# [13 14 15]
# [26 27 28]]
# [[39 40 41]
# [52 53 54]
# [65 66 67]]]- 예 6
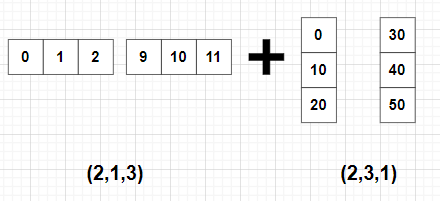
import numpy as np
A = np.arange(6).reshape((2, 1, 3))
B = 10*np.arange(6).reshape((2, 3, 1))
C = A + B
print(C)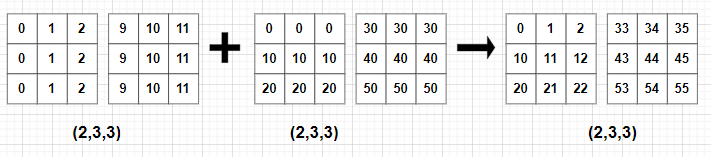
print(C) # [[[ 0 1 2]
# [10 11 12]
# [20 21 22]]
# [[33 34 35]
# [43 44 45]
# [53 54 55]]]
* 참조
- ICT이노베이션 강의 신경식 강사님 강의자료
반응형
'머신러닝 > Numpy' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Numpy] #8 axis, sum(), mean(), keepdims 기초문법 공부하기 8 (0) | 2021.10.04 |
|---|---|
| [Numpy] #7 indexing, slicing / 인덱싱, 슬라이싱 기초문법 공부하기 7 (0) | 2021.10.04 |
| [Numpy] #5 요소별 연산, 브로드캐스팅(Broadcasting) ndarray 가지고놀기 기초문법 공부하기 5 (0) | 2021.09.28 |
| [Numpy] #4 reshape(-1), flatten(), copy(), ndarray 가지고놀기 기초문법 공부하기 4 (0) | 2021.09.28 |
| [Numpy] #3 무작위, 랜덤, 표본추출 (normal, random) 기초문법 공부하기 3 (0) | 2021.09.28 |

댓글